Incorrect ....Please see the correct answer highlighted
Correct: Metastatic cystic squamous cell carcinoma
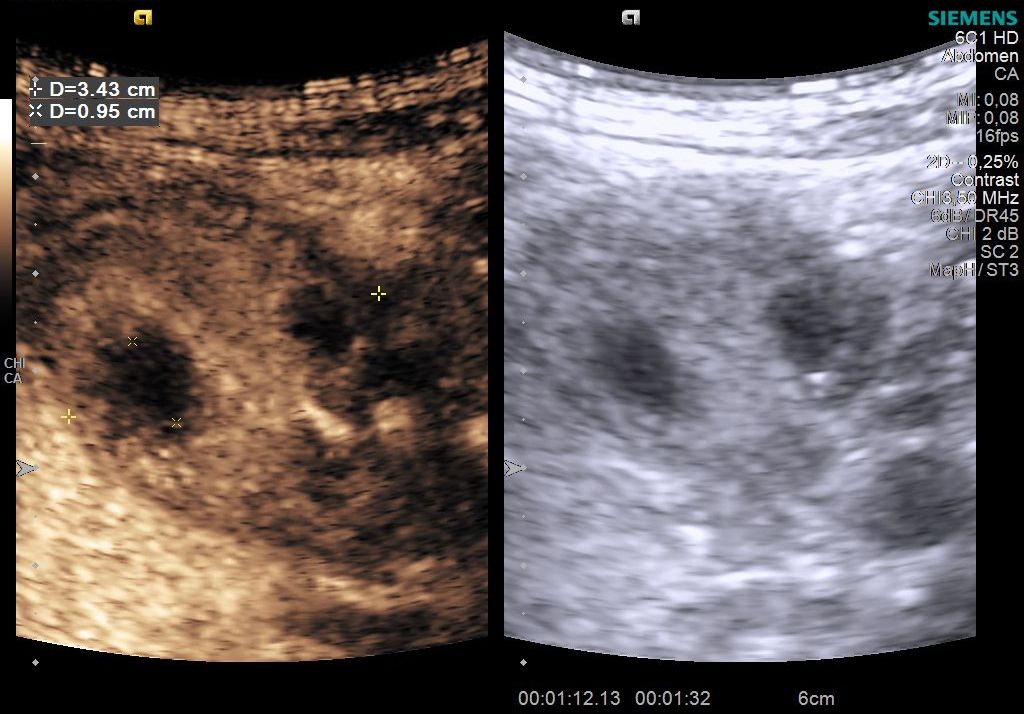
B mode ultrasound - Cervical cystic lesions, some with impure liquid content (image 2), others with a papillary solid component, with minimal Doppler signal (image 3). The lesions occupy large portions of the cervical lodge, but do not modify the adjacent space. There is no suspicious adjacent lymphadenopathy. (image 4-6).
CEUS shows a homogeneous enhancement of the solid component of the cyst (image 7) and non-enhancement of the impure cystic formations (image 8).
Also, B mode ultrasound reveals a solid hypoechoic lesion of the tongue (image 9), demonstrated after biopsy as malignant (squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue).
How to characterize the cervical lesions? Branchial cleft cysts? Cystic metastases of the squamous cell carcinoma? A second neoplasm?
The patient underwent ultrasound-guided cyst aspiration (image 10) and then biopsy of the solid component (image 11). Biopsy result showed non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium and inflammatory cells in cytology, with no elements of malignancy. Cystic formations recurred quickly, in a few days, with the initial aspect (image 12). The cysts were surgically removed and the patient was referred to oncology.
Conclusion: Latero-cervical cystic metastases secondary to squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue. Differential diagnosis is difficult taking into consideration other cervical congenital cystic structures.